Current Projects
How is changing climate and other stressors affecting agricultural water users in the Colorado River Basin?
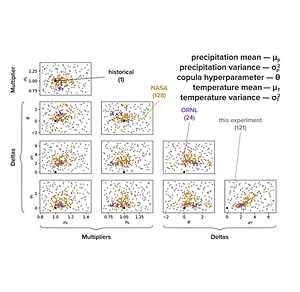
Changes in the relationship between precipitation and temperature due to climate change threaten water scarcity by increasing evapotranspiration and reducing runoff and soil moisture, with significant implications for agriculture. In the Upper Colorado River Basin, rising temperatures, earlier snowmelt, and decreased streamflow exacerbate water management challenges under prior-appropriation water rights. To address this, we developed a stochastic weather generator for use in exploratory modeling. This approach quantifies hydroclimatic impacts on agricultural water users while considering institutional constraints, and supports conservation planning for a deeply uncertain future.
Graduate Student: Alexander Thames
How is climate change and agricultural pumping affecting well salinization in Dover, Delaware?
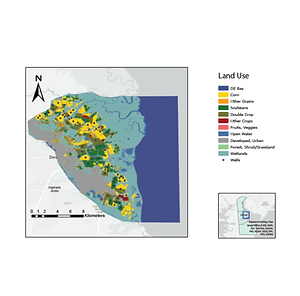
Groundwater extraction is vital for municipal, industrial, domestic, and agricultural use worldwide, but coastal aquifers face the growing threat of saltwater intrusion, rendering them unsuitable for use. This issue is particularly critical in Dover, Delaware, where coastal farmers rely on the Columbia Aquifer for irrigation amidst rising sea levels and climate change, which exacerbate salinization risks. Using downscaled climate projections and the numerical model SEAWAT, this study explores how varying recharge, pumping, and sea level rise conditions affect saltwater intrusion. The findings identify vulnerable wells and highlight scenarios with undesirable outcomes, informing strategies to protect water resources for future use.
Graduate Student: Madison Hernandez
How can co-designed adaptation strategies mitigate urban flooding in Baltimore, Maryland?
Urban pluvial flooding is an increasing concern in the Mid-Atlantic region of the USA due to climate change, increased impervious areas, and aging infrastructure. Adapting to these risks is crucial for building resilience, but uncertain future climate and conflicting stakeholder objectives complicate strategy selection. This study addresses these challenges through a community-informed and dynamic robust decision making process. By engaging community stakeholders and employing machine learning approaches, the study aims to create adaptable flood management strategies aligned with local values, and provide guidance for addressing urban flooding in Baltimore.
Graduate Student: Ava Spangler

How ran Flash drought events be detected to inform adaptive water management?
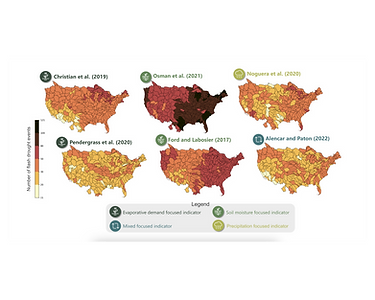
Unlike traditional droughts that develop over months or years, flash droughts emerge rapidly—sometimes within weeks or even days. These events are marked by a sudden drop in precipitation, declining soil moisture, and increased evapotranspiration. Because of their rapid onset condition, flash droughts often leave water managers and other stakeholders unprepared, providing limited time for response and adaptation. Despite growing recognition of flash droughts, key challenges remain. There is no universally accepted definition, and existing criteria often fail to capture the full range of events, leading to underdetection and gaps in understanding. This study evaluates six different flash drought indicators and assesses how well they align across regions. It also considers how different water-use sectors experience and respond to these events, integrating this information into a framework to support adaptive water management .
Post Doc: Gabriela Gesualdo
How can reservoir releases control saltwater intrusion in Havre de Grace, Maryland?
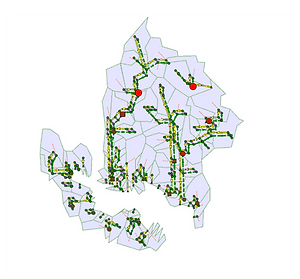
Saltwater intrusion is an emerging problem in coastal communities across the globe due to rising sea level, excessive groundwater pumping, and diminished freshwater discharges from riverine systems due to climate change. In the Chesapeake Bay, low-flows on the Susquehanna River can result in saltwater intrusion into fresh drinking water supplies. To tackle this emerging problem, we are using a multi-objective reservoir operations model to discover reservoir release policies that dilute salty drinking water for impacted communities while also meeting existing multi-sectoral demands for the reservoir’s water resources. By expanding an existing modeling framework, we are improving the resiliency of coastal water resources to emerging water quality concerns.
Graduate student: Ethan Heidtman